Selected Tai Chi Research and Benefits
An RCT META analysis based on the effect of tai chi exercise therapy on the outcome of elderly patients with moderate-to-severe sleep disorders-A systematic review study. This study provides a practical approach to reducing the risk of medication side effects in older adults with sleep disorders and offers a potentially effective non-pharmacological treatment option, especially for those who are unable or unwilling to use medication. Tai chi exercise may not only improve sleep, but also improve coordination, muscle strength, balance, and reduce stress and anxiety in older adults. It also helps older adults socialize and enhances their social connections and emotional support. This study suggests that community centers or activity centers for the elderly can organize tai chi classes to promote the participation of older adults, and can be used as a scientific exercise rehabilitation tool in clinical treatment, incorporating tai chi practice into daily life, such as tai chi practice at a fixed time every day or every week, which not only helps to improve the sleep disorders of older adults, but also improves their overall quality of life. PMCID: PMC10826669.
American College of Physicians recommends Tai Chi for lower back pain.
Tai Chi for Chronic Illness Management: Synthesizing Current Evidence from Meta-Analyses of Randomized Controlled Trials. Tai Chi improves physical function, disease-specific outcomes and cardiorespiratory fitness compared with active controls among adults with diverse chronic illnesses. [PMID 32946848]
Evidence on physical activity and falls prevention for people aged 65+ years: systematic review to inform the WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. This study found that effective exercise programs should be implemented at scale. Tai Chi was one of the most effective exercise programs for reducing rate of falls. The highest rate of benefit was "from programs involving multiple types of exercise (commonly balance and functional exercises plus resistance exercises). Note that the American College of Sports Medicine recommends Qigong and Tai Chi because they are multifaceted physical activities which involve varying combinations of neuromotor exercise (sometimes called functional fitness training, which incorporates motor skills such as balance, coordination, gait, and agility, and proprioceptive training), resistance exercise, and flexibility exercise. This research presents a very strong argument for practicing Qigong and Tai Chi to reduce rate of falls in older adults. [PMCID: PMC7689963]
The effect of Tai Chi exercise on postural time-to-contact in manual fitting task among older adults. The authors identify postural stability as the main reason for long-term Tai Chi exercise’s ability to lower the risk of falling among healthy older adults. [PMID 32896796].
How to mitigate coronavirus stress with mind-body training like Tai Chi.

Tai Chi for Neurological Conditions: The Research Evidence-Base. "Tai Ji Quan is a viable antihypertensive lifestyle therapy that produces clinically meaningful blood pressure (BP) reductions among individuals with hypertension. Such magnitude of BP reductions can lower the incidence of cardiovascular disease by up to 40%."
Tai Ji Quan as Antihypertensive Lifestyle Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
 Biomechanical mechanism of Tai-Chi gait for preventing falls: A pilot study. The results indicate that Tai Chi gait challenges body balance and requires more muscle strength of the lower limb joints compared to regular walking gait. To cope with these challenges, the body develops neuromuscular control strategies to maintain body balance and thus reduce the risk of falls. Neuromotor exercise training is beneficial as part of a comprehensive exercise program for older persons, especially to improve balance, agility, muscle strength, and reduce the risk of falls. Note that every ten years the American College of Sports Medicine updates their Position Stand: 'Quantity and Quality of Exercise for Developing and Maintaining Cardiorespiratory, Musculoskeletal, and Neuromotor Fitness in Apparently Healthy Adults: Guidance for Prescribing Exercise.' In 2008, the ACSM started recommending Tai Chi and Qigong in their Position Stand for neuromotor fitness. ACSM: "Neuromotor exercise training, sometimes called functional fitness training, incorporates motor skills such as balance, coordination, gait, and agility, and proprioceptive training. Multifaceted physical activities such as tai ji (tai chi), qigong, and yoga involve varying combinations of neuromotor exercise, resistance exercise, and flexibility exercise. Neuromotor exercise training is beneficial as part of a comprehensive exercise program for older persons, especially to improve balance, agility, muscle strength, and reduce the risk of falls."
Biomechanical mechanism of Tai-Chi gait for preventing falls: A pilot study. The results indicate that Tai Chi gait challenges body balance and requires more muscle strength of the lower limb joints compared to regular walking gait. To cope with these challenges, the body develops neuromuscular control strategies to maintain body balance and thus reduce the risk of falls. Neuromotor exercise training is beneficial as part of a comprehensive exercise program for older persons, especially to improve balance, agility, muscle strength, and reduce the risk of falls. Note that every ten years the American College of Sports Medicine updates their Position Stand: 'Quantity and Quality of Exercise for Developing and Maintaining Cardiorespiratory, Musculoskeletal, and Neuromotor Fitness in Apparently Healthy Adults: Guidance for Prescribing Exercise.' In 2008, the ACSM started recommending Tai Chi and Qigong in their Position Stand for neuromotor fitness. ACSM: "Neuromotor exercise training, sometimes called functional fitness training, incorporates motor skills such as balance, coordination, gait, and agility, and proprioceptive training. Multifaceted physical activities such as tai ji (tai chi), qigong, and yoga involve varying combinations of neuromotor exercise, resistance exercise, and flexibility exercise. Neuromotor exercise training is beneficial as part of a comprehensive exercise program for older persons, especially to improve balance, agility, muscle strength, and reduce the risk of falls."

Effectiveness of Tai Chi for Health Promotion for Adults With Health Conditions: A Scoping Review of Meta-analyses. "Tai Chi is a form of safe, enjoyable, light-to-moderate aerobic physical activity for adults that is inexpensive to implement in diverse community settings. Adults with health conditions require physical activity for prevention of secondary impairments and over-all health promotion.This scoping review of meta-analyses elucidates "high" and "moderate" quality evidence of the effectiveness of Tai Chi in improving important outcomes for people with numerous health conditions.This information can be useful for healthcare providers who wish to recommend effective community-based physical activity to clients they are serving."

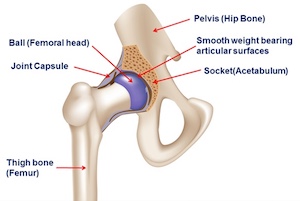
2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip, and Knee. American College of Rheumatology and the Arthritis Foundation strongly recommend Tai Chi. This is the first update of the treatment guidelines since 2012.

Qigong and Tai Chi as Therapeutic Exercise: Survey of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Addressing Physical Health Conditions. The review showed independent research evidence that was sufficient to support tai chi performed as qigong as a primary intervention for balance training and fall prevention. When compared with more traditional interventions, tai chi was found to have equal, and in some instances, superior effects, as well as cost-effectiveness. In addition, qigong, and tai chi performed as qigong, were found to have a complementary or alternative role in management of cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Parkinson's disease, and cardiac and cardiovascular disorders.
ACR, Arthritis Foundation guidelines favor nondrug therapy over TENS, stem cells for OA. ATLANTA — Health care providers should avoid prescribing transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation or stem cell injections in favor of more comprehensive management — including nonpharmacological interventions such as tai chi — for hip, knee and hand osteoarthritis, according to draft guidelines presented at ACR/ARP 2019.
 An evidence map of the effect of Tai Chi on health outcomes. The evidence map is based on a systematic review of systematic reviews. We searched 11 electronic databases from inception to February 2014, screened reviews of reviews, and consulted with topic experts. We used a bubble plot to graphically display clinical topics, literature size, number of reviews, and a broad estimate of effectiveness.
An evidence map of the effect of Tai Chi on health outcomes. The evidence map is based on a systematic review of systematic reviews. We searched 11 electronic databases from inception to February 2014, screened reviews of reviews, and consulted with topic experts. We used a bubble plot to graphically display clinical topics, literature size, number of reviews, and a broad estimate of effectiveness.

Tai Chi for Chronic Pain Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Conclusion: Clinicians may consider Tai Chi as a viable complementary and alternative medicine for chronic pain conditions.
No Pain Lots of Gain. Tai Chi and Qigong for chronic pain. The medical school textbook The Essentials of Pain Medicine 4th Edition includes an entire chapter (61) on the use of taiji for treating chronic pain conditions. This text concludes that not only is taiji a safe and effective approach to achieving a wide range of physical and psychological benefits, high- quality evidence supports the use of taiji for treating osteoarthritis, lower back pain and fibromyalgia. As promising as these findings are, it is important to remember that taiji coaches without medical credentials should not offer treatment or make treatment claims to individuals with specific conditions. Coaches can train individuals in taiji practice and educate them about findings in the literature, but it is important to leave prescriptions to health-care providers. Still, it is a great feeling being able to share in our students’ joy when they find relief from symptoms through their taiji practice!
World Taiji Science Federation Journal. JTS Journal of Taiji Science.








 Tai Chi participants improved in nearly all measures, whereas controls did not. Older adults' participation in a community-based Tai Chi program leads to improvement in strength, mobility, and confidence in performing functional tasks.
Tai Chi participants improved in nearly all measures, whereas controls did not. Older adults' participation in a community-based Tai Chi program leads to improvement in strength, mobility, and confidence in performing functional tasks.








 International Tai Chi Chuan Symposium: Interview with Dr. Roger Jahnke (Audio: 1hr 5min)
International Tai Chi Chuan Symposium: Interview with Dr. Roger Jahnke (Audio: 1hr 5min)